
The immobilization of peptides using amines isn’t always the optimal choice. Instead, functional groups such as thiol can be utilized to direct coupling processes away from active centers or binding sites on specific protein molecules. Employing a unique active group for site-directed immobilization can also aid in the correct orientation of small antigens, such as using sulfhydryl on a single terminal cysteine in a peptide.
The BcMag™ Peptide Conjugation Kit is an advanced solution designed to covalently immobilize small peptides rapidly and efficiently through their sulfhydryl groups (-SH) for use in affinity purification procedures. To conjugate small peptides, the kit recommends using BcMag™ Long-arm Iodoacetyl-activated Magnetic Beads, which feature a long-arm hydrophilic linker to reduce steric hindrance.
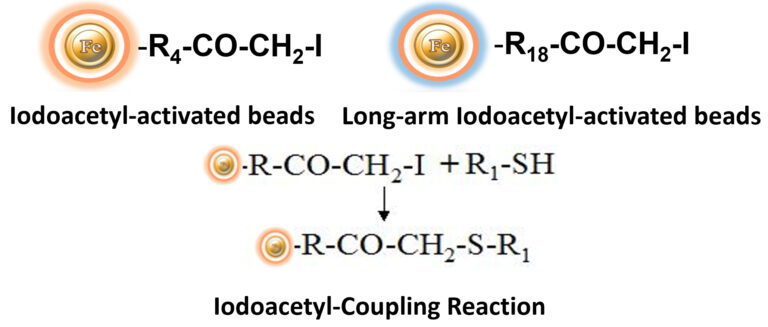
The beads themselves are uniform and silica-based superparamagnetic beads coated with a high density of Iodoacetyl or cleavable Iodoacetyl functional groups on the surface. Under physiological to alkaline circumstances (pH 7.2 to 9) in either aqueous or organic solvents containing 20-30% DMSO or DMF, iodoacetyl-activated supports react with sulfhydryl groups to form stable thioether bonds. These reactions are typically performed in the dark to prevent the formation of free iodine, which can react with tyrosine, histidine, and tryptophan residues.
Workflow
The Iodoacetyl magnetic beads work perfectly as solid support for various bioseparations to refine molecules, cells, and parts of cells into purified fractions. After conjugation with ligands, add the beads to a solution containing the target molecules, then mix, incubate, wash and elute the target molecules.
Features and benefits
●
Iodoacetyl groups react selectively with sulfhydryl (-SH) groups to produce irreversible thioether linkages.
●
Fast – couple peptide samples in 2 hours.
●
Versatile coupling conditions – as needed for protein or peptide solubility during the coupling reaction, employ pH 7.5 to 9.0 aqueous buffers, organic solvent (e.g., 20% DMSO), or denaturant (guanidineHCl).
●
Simple to follow protocols for sample preparation, immobilization, and affinity purification
●
High capacity – Immobilize 15-20μg antibody/mg beads
Applications
●
Immobilize peptides with terminal cysteine residues to purify antibodies raised against peptide immunogens.
●
Immobilize antibodies in an orientated manner using hinge-region sulfhydryl to ensure that antigen binding sites are not sterically inhibited when antigen affinity purification is performed.
●
Produces reusable immunoaffinity matrices
●
Maintains antibody function – immobilizes IgG via the Fc region, leaving both antigen binding sites available for target capture.
PROTOCOL
Note:
●
This protocol can be scaled up as needed. We strongly recommended titration to optimize the number of beads used for each application.
Materials Required
●
Coupling Buffer
1.
Soluble coupling buffer: 50 mM Tris, 5 mM EDTA-Na, pH 8.5
2.
Insoluble coupling buffer: 50 mM Tris, 5 mM EDTA-Na, pH 8.5, 20- 30% DMSO or DMF or 6 M guanidine•HCl
●
Wash Buffer: 1 M sodium chloride (NaCl) in distilled H2O●
L-Cysteine•HCl
●
TCEP (tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine)
●
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
●
2.5μm Long-arm Iodoacetyl-activated Magnetic Beads.
●
Magnetic Rack (for manual operation)
Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following Magnetic Racks:
1.
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
2.
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
3.
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
4.
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
5.
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-96 for holding a 96 ELISA plate or PCR plate (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
A.
Ligand Preparation
Note:
●
Ensure that ligands have free (reduced) sulfhydryls. If free sulfhydryl groups are not available, use a reducing agent such as DTT (dithiothreitol), TCEP (tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine), or 2-MEA (2-Mercaptoethylamine•HCl) to treat ligands followed by desalting or dialysis to remove the reducing agent.
●
Newly Synthesized peptides may be directly used for coupling if used immediately after reconstitution.
●
For protein, treat protein with 5-10 mM TCEP solution for 30 minutes at room temperature, followed by dialysis or a desalting column. For IgG antibodies, 2-MEA is recommended due to its Selective reduction of hinge-region disulfide bonds.
●
If the sample contains reducing agents with free sulfhydryls (e.g., 2-mercaptoethanol or DTT), these agents must be completely removed by dialysis or desalting.
1.
Dissolve 1-10mg protein/peptide in 1ml soluble coupling buffer if soluble. If insoluble, dissolve in 1ml insoluble coupling buffer.
2.
If samples have already been suspended in other buffers, dilute samples with an equal volume of coupling buffer.
B.
Magnetic Beads Preparation
1.
Prepare 3% magnetic beads with 100% Acetone (30 mg/ml).
Note: Store the unused beads in acetone solution at 4°C. It has been stable for over a year.
2.
Transfer 100 μl (3mg) magnetic beads to a centrifuge tube.
3.
Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack. Remove the tube from the rack and resuspend the beads with 1 ml coupling buffer by vortex for 30 seconds.
4.
Repeat step 3 two times.
5.
Remove the supernatant, and the washed beads are ready for coupling.
Note: Once rehydrated using the coupling buffer, use the bead as soon as possible due to the stability of the functional group.
C.
Coupling
1.
Add 100 μl of ligand to the washed beads, mix well and incubate the sample in the dark at room temperature overnight with good mixing (end-over-end)
2.
Wash the magnetic beads with 1ml coupling buffer four times.
3.
Block the excess active groups on the beads by suspending the beads in 1ml Coupling buffer containing 8mg L-Cysteine•HCl and incubate 30-60 minutes at room temperature with gentle rotation.
4.
Wash the beads with 1ml washing buffer four times.
5.
Resuspend the beads in PBS buffer containing 0.05% sodium azide and store them at 4°C.
D.
General affinity purification Protocol
Note:
●
This protocol is a general affinity purification procedure. Designing a universal protocol for all protein purification is impossible because no two proteins are precisely alike. To obtain the best results, the user should determine the optimal working conditions for purifying the individual target protein.
●
Avoid reducing agents in binding and washing buffers.
●
We strongly recommended titration to optimize the number of beads used for each application based on the amount of the target protein in the crude sample. Too many magnetic beads used will cause higher backgrounds, while too few beads used will cause lower yields. Each mg of magnetic beads typically binds to 10-20 μg of target protein.
1.
Transfer the optimal amount of the beads to a centrifuge tube. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
2.
Remove the tube and wash the beads with 5-bed volumes of PBS buffer by vortex for 30 seconds. Leave the tube at room temperature for 1-3 minutes. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
3.
Repeat step 2 two times.
4.
Add washed beads to the crude sample containing the target protein and incubate at room or desired temperature for 1-2 hours (Lower temperatures require longer incubation time).
Note: Strongly recommended to perform a titration to optimize incubation time. More prolonged incubation may cause higher background.
5.
Extensively wash the beads with 5-beads volumes of PBS buffer or 1M NaCl until the absorbance of eluting at 280 nm approaches the background level (OD 280 < 0.05).Note: Adding a higher concentration of salts, nonionic detergent, and reducing agents may reduce the nonspecific background. For example, adding NaCl (up to 1-1.5 M), 0.1-0.5% nonionic detergents such as Triton X 100 or Tween 20 to the washing buffer.
6.
Elute the target protein by appropriate methods such as low pH (2-4), high pH (10-12), high salt, high temperature, affinity elution, or boiling in SDS-PAGE sample buffer, or reducing agents.
Learn More
Instruction Manual
MSDS
Related Antibody Magnetic Beads →


